coding error case
May 11, 2025
Camille X
error fix experience
2 / 2 Parts
题目
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def pathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], targetSum: int) -> int:
prefix_counter = Counter()
ans = 0
def dfs(root, prefix):
nonlocal ans
if not root:
return
prefix += root.val
prefix_counter[prefix] += 1
if prefix - targetSum in prefix_counter:
ans += prefix_counter[prefix - targetSum]
dfs(root.left, prefix)
dfs(root.right, prefix)
dfs(root, 0)
return ans
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def pathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], targetSum: int) -> int:
prefix_counter = Counter()
ans = 0
def dfs(root, prefix):
nonlocal ans
if not root:
return
prefix += root.val
prefix_counter[prefix] += 1
if prefix - targetSum in prefix_counter:
ans += prefix_counter[prefix - targetSum]
dfs(root.left, prefix)
dfs(root.right, prefix)
dfs(root, 0)
return ans
这段代码的三个典型错误
- base case
在前缀和问题中,我们通常需要初始化 prefix_counter[0] = 1,表示「从根节点到当前位置的路径和正好等于 target」的情况,否则从根节点直接开始的路径不会被统计。
- 前缀和统计方式错误
如果target == 0, 只有一个节点非0,if prefix - targetSum in prefix_counter统计的是从当前到之前某个节点的路径,不包含之前的那个节点,如果按照先加入再统计,那就把之前的节点包含进来了
- 回溯时没有撤销当前节点的前缀和
左右都看完后,当前节点需要返回,但是不需要当前节点的值了。
题目
406. Queue Reconstruction by Height
class Solution:
def reconstructQueue(self, people: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
people.sort(key = lambda x: -x[0])
#=> people.sort(key = lambda x: (-x[0], x[1]))
for i, (h, rank) in enumerate(people):
if i == rank:
continue
j = i
while j != rank:
tmp = people[j]
people[j] = people[j - 1]
people[j - 1] = tmp
j -= 1
return people
class Solution:
def reconstructQueue(self, people: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
people.sort(key = lambda x: -x[0])
#=> people.sort(key = lambda x: (-x[0], x[1]))
for i, (h, rank) in enumerate(people):
if i == rank:
continue
j = i
while j != rank:
tmp = people[j]
people[j] = people[j - 1]
people[j - 1] = tmp
j -= 1
return people
这段代码的一个典型错误
- 排序方式错误
h倒序, rank正序。[[9,0],[7,0],[1,9],[3,0],[2,7],[5,3],[6,0],[3,4],[6,2],[5,2]],由于当前值都比前面值小,挪值不会影响已经挪好的rank,如果[6, 2]在[6, 0]前,那挪动[6, 0]时就会破坏[6, 2]的rank
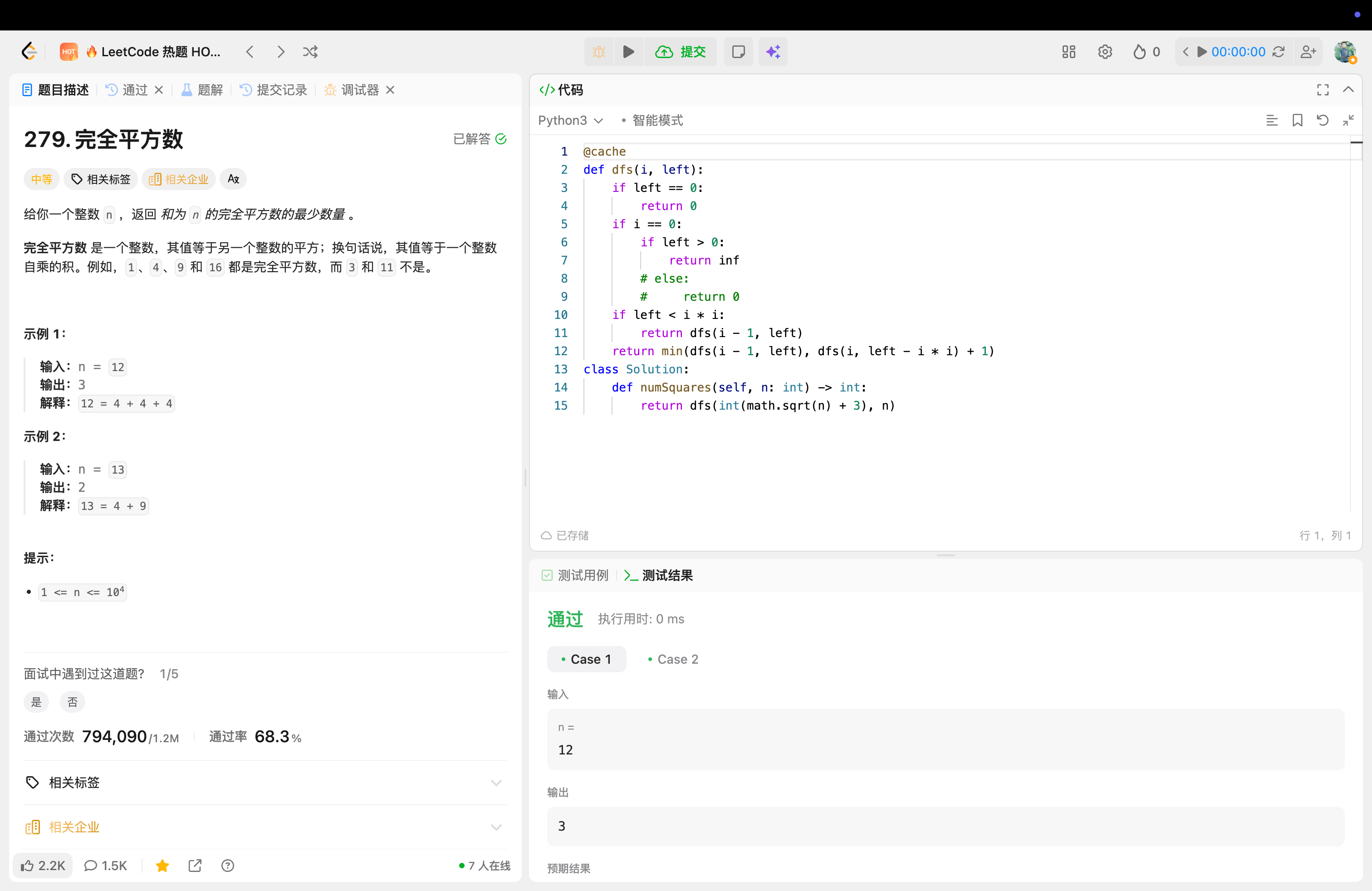
题目
class Solution:
def numSquares(self, n: int) -> int:
import math
def dfs(i, left):
if i < 1:
if left > 0:
return `float('+inf')`
else:
return 1
if left < i:
return dfs(i - 1, left)
return min(dfs(i - 1, left), dfs(i, left - i * i) + 1)
return dfs(int(math.sqrt(n) + 1), n)
class Solution:
def numSquares(self, n: int) -> int:
import math
def dfs(i, left):
if i < 1:
if left > 0:
return `float('+inf')`
else:
return 1
if left < i:
return dfs(i - 1, left)
return min(dfs(i - 1, left), dfs(i, left - i * i) + 1)
return dfs(int(math.sqrt(n) + 1), n)
这段代码的一个典型错误
边界条件错误
关键终止条件是:left == 0, 此时不需要再加1了, 直接返回0即可。
left 小于 0时,说明当前路径不可行,返回float('+inf')。left砍值(比较)错误,应该是left 小于 i i*
left不可能小于0
初始left > 0, 如果left 小于 i * i, 那么下一步就会走dfs(i - 1, left), left不会变小,所以left不可能 小于 0
i的初始值
i的初始值应该是 int(math.sqrt(n)),但是也可以是稍微大点的,毕竟如果left 小于 i * i, 也会走dfs(i - 1, left),i也会自动减小,直到math.sqrt(n)
3. Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters
class Solution:
def lengthOfLongestSubstring(self, s: str) -> int:
l, r = 0, 0
rec = defaultdict(int)
ans = 0
for r, c in enumerate(s):
if c not in rec:
rec[c] = r
else:
l = max(l, rec[c] + 1)
ans = max(ans, r - l)
return ans
class Solution:
def lengthOfLongestSubstring(self, s: str) -> int:
l, r = 0, 0
rec = defaultdict(int)
ans = 0
for r, c in enumerate(s):
if c not in rec:
rec[c] = r
else:
l = max(l, rec[c] + 1)
ans = max(ans, r - l)
return ans
这段代码的一个典型错误
- ans计算错误'
ans = max(ans, r - l + 1)
- rec[c]更新错误
无论是否在rec中,都需要更新rec[c] = r
