π0
October 10, 2024
C X
Camille X
Robotic Imitation Learning Methods
6 / 6 Parts
flow-matching method for robotics imitation learning
Series
flow-matching vs diffusion in robotics imitation learning
到目前的act的VAE, diffusion policy的u-net, pi0的flow-matching基本都源自于图像生成领域。在有条件情况下,图像的序列预测与机器人的动作序列预测有相通的地方,图像是(c, h, w), 机器人动作是(horizon, action_dim),都是多维度的连续值序列预测问题。c ~ action_dim, h*w ~ horizon。`
其实到最后,会发现act,dp, pi0最后生成的序列都是来自于一个shape为(horizon, action_dim)的采样,act是全0的query,用encoder_output作为key和value;dp和pi0,虽然都是在shape为(horizon, action_dim)的标准高斯分布中采样但也都是以state, img, env信息作为condition,可以理解为使用shape为(horizon, action_dim)的标准高斯分布作为query, 用condition作为key和value。
vla的引入解决的是常识性的问题,比如黄色胶带引起的伪关联问题。另外rl的引入或许也可以解决这部分问题。
环境信息的引入,一方面可以缓解机器人本身获取信息的局限性和不确定性,另一方面也可以提供更丰富的上下文信息,帮助模型更好地理解任务和环境,从而提升生成动作序列的质量和鲁棒性。典型的比如点云信息的引入,在工厂或者家庭环境中,机器人本身相机获取的点云信息与环境中的点云信息匹配,可以帮助机器人更好地理解其在环境中的位置和姿态,而不仅仅是基于自身的末端位置,这样可以解决视角泛化问题。
ddpm
def conditional_sample(
self, batch_size: int, global_cond: Tensor | None = None, generator: torch.Generator | None = None
) -> Tensor:
device = get_device_from_parameters(self)
dtype = get_dtype_from_parameters(self)
# Sample prior.
sample = torch.randn(
size=(batch_size, self.config.horizon, self.config.action_feature.shape[0]),
dtype=dtype,
device=device,
generator=generator,
)
# self.noise_scheduler.set_timesteps(self.num_inference_steps)
self.noise_scheduler.set_timesteps(10)
for t in self.noise_scheduler.timesteps:
# Predict model output.
model_output = self.unet(
sample,
torch.full(sample.shape[:1], t, dtype=torch.long, device=sample.device),
global_cond=global_cond,
)
# Compute previous image: x_t -> x_t-1
sample = self.noise_scheduler.step(model_output, t, sample, generator=generator).prev_sample
return sample
def conditional_sample(
self, batch_size: int, global_cond: Tensor | None = None, generator: torch.Generator | None = None
) -> Tensor:
device = get_device_from_parameters(self)
dtype = get_dtype_from_parameters(self)
# Sample prior.
sample = torch.randn(
size=(batch_size, self.config.horizon, self.config.action_feature.shape[0]),
dtype=dtype,
device=device,
generator=generator,
)
# self.noise_scheduler.set_timesteps(self.num_inference_steps)
self.noise_scheduler.set_timesteps(10)
for t in self.noise_scheduler.timesteps:
# Predict model output.
model_output = self.unet(
sample,
torch.full(sample.shape[:1], t, dtype=torch.long, device=sample.device),
global_cond=global_cond,
)
# Compute previous image: x_t -> x_t-1
sample = self.noise_scheduler.step(model_output, t, sample, generator=generator).prev_sample
return sample
- 模型预测的结果是 x_t - x_0,即噪声
- sample = x(t-1), 这里可以通过公式计算从x_t到x(t-1)的转换
- 迭代10次,逐步去噪
采样
- 计算第t步x_0的估计,根据公式, 反推x_0:
- 根据x0的估计,计算x(t-1)
ddim
- 似乎不用逐步倒退, 而是可以跳步比如从xt直接到x(t-5)
ddim vs ddpm

ddim vs ddpm
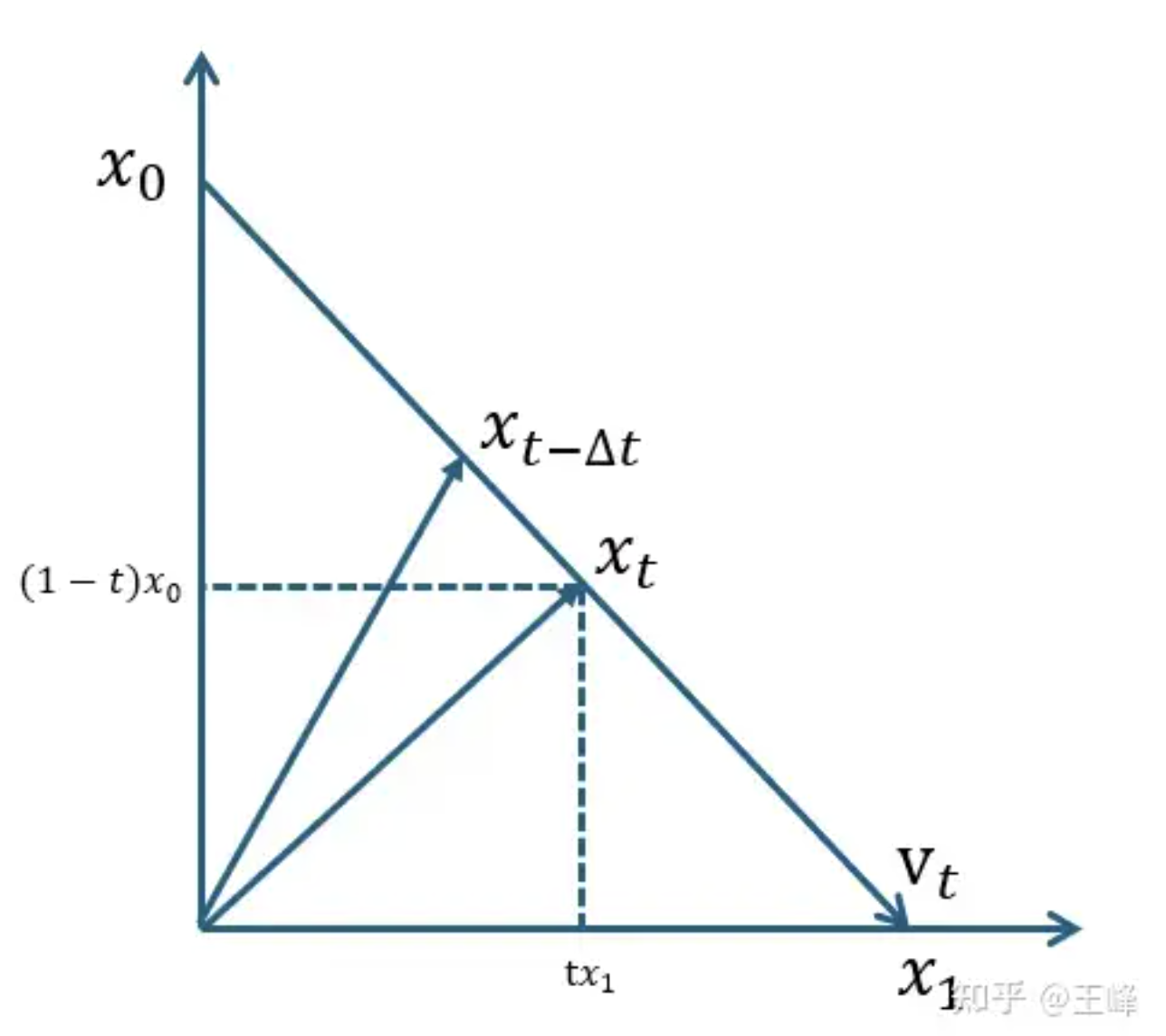
flow matching
- 模型预测的结果是噪声方向
